
The Risk of Colon Cancer in Women
Colon cancer can affect anyone regardless of race, gender, or other characteristics. While colon cancer occurs slightly more frequently in men, women are nearly as
HIPAA Alert: Potential Data Breach Learn More
Questions on Oncology, Hematology and/or Infusion Clinical Services due to COVID-19 Crisis – CALL 833-698-1623
Important Information for Our Patients Regarding the Coronavirus.
RCCA Providing Area Cancer Patients with Access to Care During Coronavirus Outbreak
RCCA Offering Patients Virtual Visits During Coronavirus Pandemic
Uterine cancer is among the most common types of cancer in the United States, with more than 65,000 cases diagnosed each year. Fortunately, uterine cancer is treatable, especially when doctors detect and treat it early.
Serving patients throughout New Jersey, Connecticut, Maryland, and the Washington, D.C., area, Regional Cancer Care Associates (RCCA) offers cutting-edge cancer treatment options. The board-certified medical oncologists at RCCA have significant experience treating uterine cancer, including endometrial cancer and uterine sarcoma. Learn more about the risk factors and symptoms of uterine cancer as well as treatment options and risk reduction.
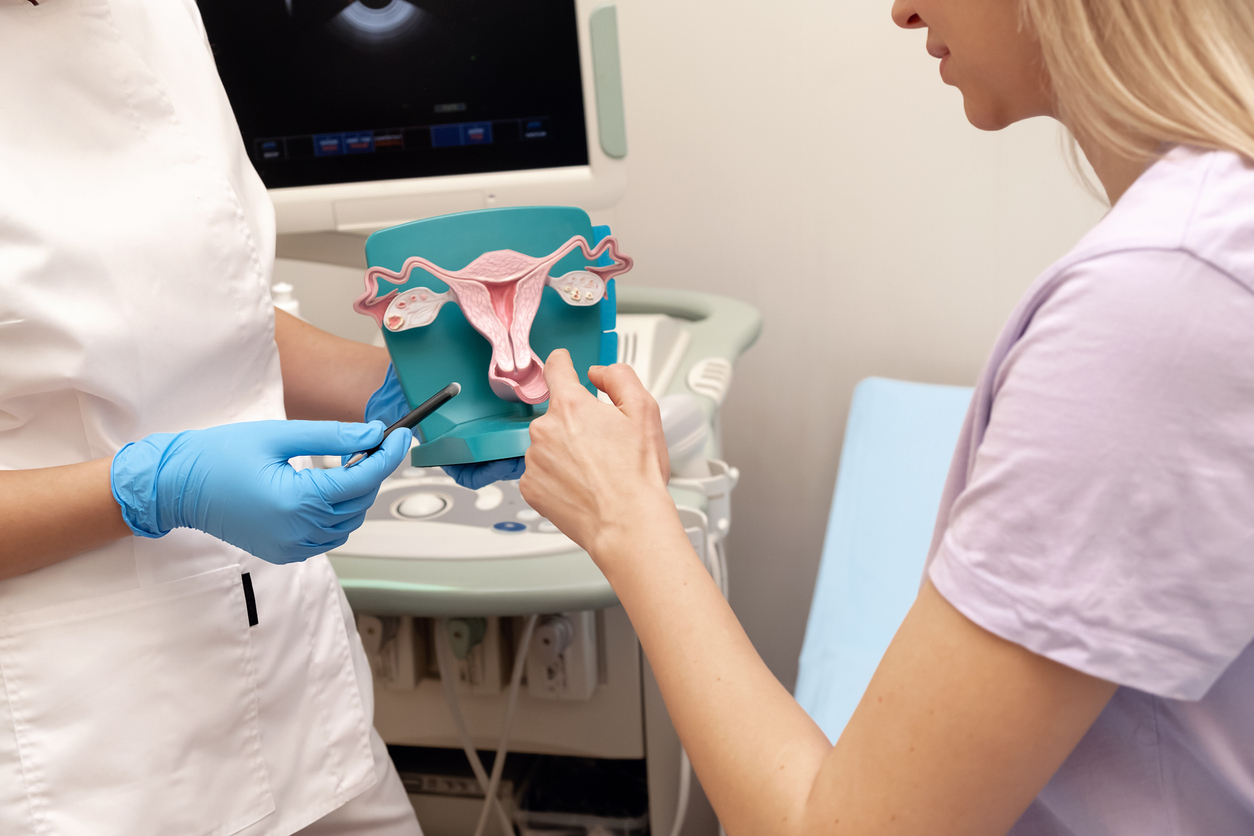
Uterine cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the tissues of the uterus or its lining, known as the endometrium. The two main types of uterine cancer are uterine sarcoma and endometrial cancer.
The uterus is a female reproductive organ located in the pelvis between the bladder and the rectum. In pregnancy, eggs that are released by the ovaries and then fertilized by sperm (which typically occurs in the fallopian tubes), move into the uterus. Each month during a woman’s reproductive years (after puberty and before menopause), the lining of the uterus thickens to prepare for pregnancy. If an egg is not fertilized and pregnancy does not occur, the uterus sheds its lining – the endometrium – causing a menstrual period.
The two main types of uterine cancer are:
Endometrial cancer is the most common uterine cancer, accounting for more than 90% of cases. Endometrial cancer originates in the tissues of the endometrium. The first sign of this type of cancer is often irregular bleeding. It is not clear what causes endometrial cancer to develop, but certain hormonal changes and hormone therapies can increase risk.
Uterine sarcoma is rare and accounts for less than 4% of all uterine cancers in the United States. This type of uterine cancer typically develops in the muscle wall of the uterus, known as the myometrium. Uterine sarcoma usually grows and spreads more quickly than other cancers of the uterus.
Certain factors increase a person’s risk of uterine cancer. These include:
A personal history of cancer can also raise a patient’s risk. Women who have had breast cancer, colon cancer, or ovarian cancer may have an inherited risk for uterine cancer.

Symptoms of uterine cancer include:
● Abnormal bleeding or spotting, including vaginal bleeding between periods or after menopause
Patients experiencing abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge should see their doctor right away.
In addition to a pelvic exam, several tests are used to confirm a diagnosis of uterine cancer:
If cancer cells are detected, a patient may need additional imaging tests such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess how far the cancer has progressed, a process known as staging.
Once uterine cancer is detected, physicians determine its stage. Stages range from I to IV, with IV being the most advanced. Staging is determined by assessing the primary tumor, checking whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, and determining if the cancer has metastasized, meaning it has spread to other parts of the body. The stages of uterine cancer are:
Staging helps determine the best treatment approach. When cancer is detected early, it is easier to treat. In the U.S., the overall five-year survival rate for uterine cancer is 81%. For endometrial cancer that has not spread outside the uterus, the five-year survival rate is as high as 96%.

Typically, surgery is the primary treatment for uterine cancer. One option is a total hysterectomy, which is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. This may be performed as a minimally invasive procedure or as traditional (open) surgery. In some cases, the ovaries and fallopian tubes will be removed, as well.
During a hysterectomy, surgeons may also perform a lymph node dissection, known as a lymphadenectomy. They will check one of the lymph nodes closest to the uterus to see if cancer cells are present. This is known as a sentinel node biopsy. If the biopsy reveals malignant cells, it is an indication that the cancer may have spread to other lymph nodes. If the lymph node is cancer-free, it is unlikely that lymph nodes in other parts of the body have cancer.
Another option is hormone therapy, which is often used in conjunction with surgery or other forms of treatment. Hormone therapy drugs work by suppressing the hormones that help cancer grow or by interfering with hormonal function. Other methods for treating uterine cancer include:
These may be used as adjuvant treatments, meaning they are administered after surgery to reduce the likelihood that cancer remains or comes back.
As with any form of cancer, patients may struggle to cope with a uterine cancer diagnosis. Treatment can take a physical and emotional toll, so patients need to understand the psychological impact of a cancer diagnosis and seek emotional support when needed. Healthcare providers can offer referrals to support groups and counseling resources, as well as recommend lifestyle changes or complementary therapies that may be helpful.
While it may not be possible to prevent uterine cancer, there are steps patients can take to reduce their risk. These include:
Birth control pills may also help decrease the risk of uterine cancer by regulating hormone levels.
Treatment for uterine cancer typically involves a hysterectomy. However, patients who have early-stage, slow-growing adenocarcinoma and want to have a child may be treated initially with hormonal therapy instead. After giving birth, removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries may be recommended. Because treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can also affect the reproductive system, all patients who have been diagnosed with any type of cancer should talk with their provider about options for preserving their fertility.
Some frequently asked questions regarding uterine cancer are:
There is no definitive way to prevent uterine cancer, but patients can lower their risk through several steps, including maintaining a healthy weight.
Unusual vaginal bleeding or an abnormal Pap smear are often the earliest signs of uterine cancer.
Uterine cancer may be diagnosed using a biopsy or other tests.
Surgery, in the form of a partial or total hysterectomy, is often the best treatment option for uterine cancer. Other treatment options include hormone therapy, radiation, and chemotherapy. These may be administered following hysterectomy.
Some hereditary conditions, such as Lynch syndrome and Cowden syndrome, can increase a patient’s chance of developing uterine cancer.
Yes. After a hysterectomy, a patient will no longer be able to become pregnant. Patients may be able to freeze their eggs before surgery but will need a surrogate or gestational carrier in the future.
The best defense against uterine cancer is early detection and intervention. Patients are encouraged to talk with their healthcare providers whenever they notice unusual bleeding or related symptoms. For patients who have been diagnosed with uterine cancer, comprehensive care is available from the doctors at RCCA. The knowledgeable medical oncologists serve patients in New Jersey, Connecticut, Maryland, and the Washington, D.C., area at over 20 locations. The experienced medical team provides treatment for all cancer types, as well as blood disorders. For more information about cancer care at RCCA, contact us today.
For expert uterine cancer diagnosis and treatment close to home, consider Regional Cancer Care Associates (RCCA). We are one of the largest cancer care networks in the country. We’re located in several states—yet we focus on every patient, individually. At RCCA, you’ll receive advanced, dedicated and compassionate cancer care. We work with you and your family to deliver care that’s second to none.
Schedule an appointment with RCCA by calling the RCCA location nearest you. You can also get in touch by calling (844) 346-7222.

Colon cancer can affect anyone regardless of race, gender, or other characteristics. While colon cancer occurs slightly more frequently in men, women are nearly as

A family history of cancer can be intimidating, because it means your risk of getting the disease may be higher compared to those with no

Colon cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related death among US men and women combined, the American Cancer Society (ACS) says. But there
When standard cancer treatments aren’t providing the results you want, clinical trials may offer hope. Our physicians use clinical trials to study new treatments, helping transform cancer care for the better. You can enroll in a clinical trial to try groundbreaking treatment plans at zero cost to you.

Regional Cancer Care Associates is one of fewer than 200 medical practices in the country selected to participate in the Oncology Care Model (OCM); a recent Medicare initiative aimed at improving care coordination and access to and quality of care for Medicare beneficiaries undergoing chemotherapy treatment.