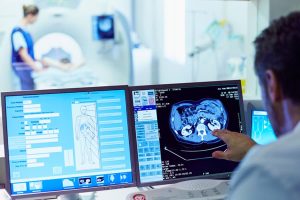
PSMA Therapy for Metastatic Prostate Cancer
A targeted, infused therapy that delivers radiation directly to cancerous cells has been shown to extend survival in many patients with metastatic prostate cancer. The
HIPAA Alert: Potential Data Breach Learn More
Questions on Oncology, Hematology and/or Infusion Clinical Services due to COVID-19 Crisis – CALL 833-698-1623
Important Information for Our Patients Regarding the Coronavirus.
RCCA Providing Area Cancer Patients with Access to Care During Coronavirus Outbreak
RCCA Offering Patients Virtual Visits During Coronavirus Pandemic
Brain cancer can be life-threatening, but early detection allows patients to receive effective treatment promptly and increases the likelihood of favorable outcomes. Early detection depends, in part, on patient awareness of the risk factors for brain cancer. At Regional Cancer Care Associates, our expert team of oncologists and hematologists treat many cancers and blood disorders – including brain cancer – providing comprehensive, cutting-edge, and compassionate care for patients in New Jersey, Connecticut, Maryland, and the Washington, D.C., area. Learn more about brain cancer risk factors from Regional Cancer Care Associates.
The cause of brain cancer is not clear in every case. However, physicians have identified several risk factors that increase the likelihood that a person will develop the disease, including:
If a person has blood relatives who have had a brain tumor, he or she may be more likely to develop brain cancer.
As valuable as radiation therapy is for treating many cancers, individuals exposed to frequent radiation may be at increased risk for brain cancer. Patients who undergo radiation therapy for cancer must be mindful of brain cancer symptoms and seek medical evaluation promptly.
Even without having received radiation therapy, simply having cancer in the past can increase the possibility of developing a brain tumor. When a patient has or previously had cancer in another part of the body, that cancer may spread to the brain. It’s important to monitor symptoms and be monitoring regularly to ensure cancer has not migrated to other parts of the body.
Some cancers may be more prevalent in one sex than the other. For example, men are at higher risk than women for developing brain tumors overall, but women have a greater chance of developing certain specific , such as meningioma.
While brain tumors typically affect older adults, they also develop in children.
The signs of a brain tumor differ depending on the location and size of the cancer. Larger, more severe tumors or tumors in certain areas of the brain affect different parts of the body. However, people with smaller tumors may be asymptomatic – particularly in the early stages of the tumor’s development. People with brain tumors may experience the following symptoms:
It is important to note that these symptoms may reflect a wide variety of causes. However, all require medical evaluation.
Physicians typically categorize brain tumors into four grades:
While survival rates for people with brain cancer depend on several factors, one trend remains consistent: The sooner a patient receives treatment, the better the results are likely to be. Treatment for brain cancer varies depending on the tumor size and location, as well as factors including the patient’s overall health. Smaller tumors and those located in areas of the brain that are easy to access usually are better suited to surgical intervention than other types of tumors. Brain cancer treatments include:
The experienced team at Regional Cancer Care Associates provides patients with comprehensive, cutting-edge, and compassionate treatment for a host of cancers and blood disorders, including brain tumors. To learn more about our patient-focused care in New Jersey, Connecticut, Maryland, and the Washington, D.C., area, contact us today.
Doctors at Regional Cancer Care Associates (RCCA) are specialists in brain cancer. These experts have proven their leadership as professors, clinicians and researchers and were trained at the world’s most distinguished medical institutions. RCCA offers high-quality, advanced treatment near your home. We work with you and your family to make sure your care is second to none.
You can set up an appointment by calling the RCCA location nearest you. Or, for more information, call (844) 346-7222.

A targeted, infused therapy that delivers radiation directly to cancerous cells has been shown to extend survival in many patients with metastatic prostate cancer. The

Patients receiving treatment from Regional Cancer Care Associates in Moorestown are in good hands. Five of its physicians — Dr. Seth Berk, Dr. Maurice Cairoli, Dr.

The world of cancer treatment is rapidly evolving. New therapies are being discovered, and existing ones have improved, resulting in better patient outcomes. Regional Cancer

Regional Cancer Care Associates is one of fewer than 200 medical practices in the country selected to participate in the Oncology Care Model (OCM); a recent Medicare initiative aimed at improving care coordination and access to and quality of care for Medicare beneficiaries undergoing chemotherapy treatment.